Describe the Two Main Types of Mutations
Induced mutations are those that result from an exposure to chemicals UV rays x-rays or some other environmental agent. Mutations are permanent heritable changes in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome.
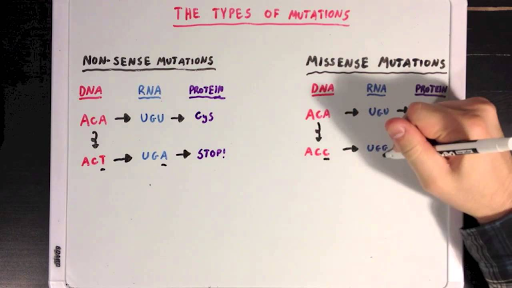
The Different Types Of Mutations Video Khan Academy
As a result the protein made by the gene may not function properly.
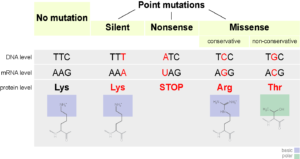
. Instead of substituting one amino acid. Chromosomal mutations a change in the number or structure of an entire chromosome. This type of mutation may alter the function of the resulting protein.
The mutations are of three types. Once DNA proofreading is completed the cell proceeds to the next stage of the cell cycle. A point mutationthe change of a single nitrogen base in a DNA sequence is usually the least harmful.
A frameshift mutation results from an insertion or deletion of a number of nucleotides that is not a multiple of three. It refers to any change in the sequence of DNA which has no further impact on the amino acid sequence in a protein or in the functions performed by a protein. If the chromosomes are not split correctly there may be mutations that affect the entire genetic makeup of the cells.
Frameshift mutations are generally much more serious and often more deadly than point mutations. Physical mutagens include various types of radiation viz. Types and Examples of DNA Mutations Point Mutations.
A deletion mutation occurs when a nucleotide is skipped or absent from the replicated strand. Those that produce changes in whole chromosomes are known as chromosomal mutations. Cells have a finely tuned mechanism for correcting mutations at checkpoints during cell division which detects most mutations.
Insertions deletions and duplications can all be frameshift mutations. These changes may be mutations in DNA or they could be mistakes that happen during mitosis or meiosis in relation to the chromosomes. Describe the 2 main types of mutations.
Describe the two main types of mutation within a gene. Explain the outcomes of germ cell mutation. X-rays gamma rays alpha particles beta particles fast and thermal slow neutrons and ultra violet rays Table 252.
Listed below are the types of mutations. This type of mutation occurs when the addition or loss of DNA bases changes a genes reading frame. Nonsense mutations produce truncated and frequently nonfunctional proteins.
Includes deletions duplications inversions and translocations deletion chromosomal. An insertion changes the number of DNA bases in a gene by adding a piece of DNA. Depending on the role of the amino acid in the protein this mutation will have greater or lesser severity.
Nonsense mutations meaningless are those in which the mutation rather than inducing the change of one protein for another causes a halt in the construction of the protein. They are a result of natural reactions taking place within the body. Those that produce changes in a single gene are known as gene mutations.
Missense mutations may retain function depending on the chemistry of the new amino acid and its location in the protein. Mutagens are of two types viz. Two major types of mutation.
The two main types of mutations are gene mutations which can either be point mutations happening in a single or a few nucleotides or frameshift mutations when a nucleotide or nucleotides are inserted or deleted and chromosomal mutations which involves changes in the structure or number of the entire chromosome. Insertions are mutations in which extra base pairs are inserted into a new place in the DNA. Since protein-coding DNA is divided into codons three bases long insertions and deletions can alter a gene so that its message is no longer correctly parsed.
Another type of mutation is a frameshift mutation. Mutation within a gene. Deletions are mutations in which a section of DNA is lost or deleted.
Why was this mutation important to the human. Mutation within regulatory DNA. A nonsense mutation is also a change in one DNA base pair.
An insertion occurs when an extra nucleotide is incorporated into the DNA sequence during replication. A duplication consists of a piece of DNA that is abnormally copied one or more times. Gene mutations and chromosomal mutations are two broad categories in which the mutation is classified.
Describe the positive outcome of mutation to the regulatory DNA for the expression of the lactase gene. Types of Mutations Missense mutation. These are discussed as follows.
One type of mutation is called a point mutation in which one nitrogen base in a sequence is substituted for another. A nonsense mutation is also a change in one DNA base pair. Definition of mutation.
The change in reading frame alters every amino acid after the. What are their overall effects on a genome. Types of mutations.
Spontaneous mutations occur without any exposure to any environmental agent. Gene mutation examples include severe genetic disorders cell overgrowth tumor formation and heightened risk of breast cancer. 1 Physical mutagens and 2 Chemical mutagens.
These mutations are often considered more harmful than substitutions because they impact upon the way the rest. There is no phenotypic indicator of mutation. All mutations fall into 2 basic categories.
A reading frame consists of groups of 3 bases that. Such mutations may be of two types. This type of mutation is a change in one DNA base pair that results in the substitution of one.
Insertions and deletions are two other types of point mutations. Microevolution is based on the changes at a molecular level that cause species to change over time. By the replication errors exposure to mutagens and viral infections change or alteration occurs in a DNA sequence that causes genetic abnormalities known as mutation.

Types Of Mutations Mt Hood Community College Biology 102

Types Of Mutations Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy


No comments for "Describe the Two Main Types of Mutations"
Post a Comment